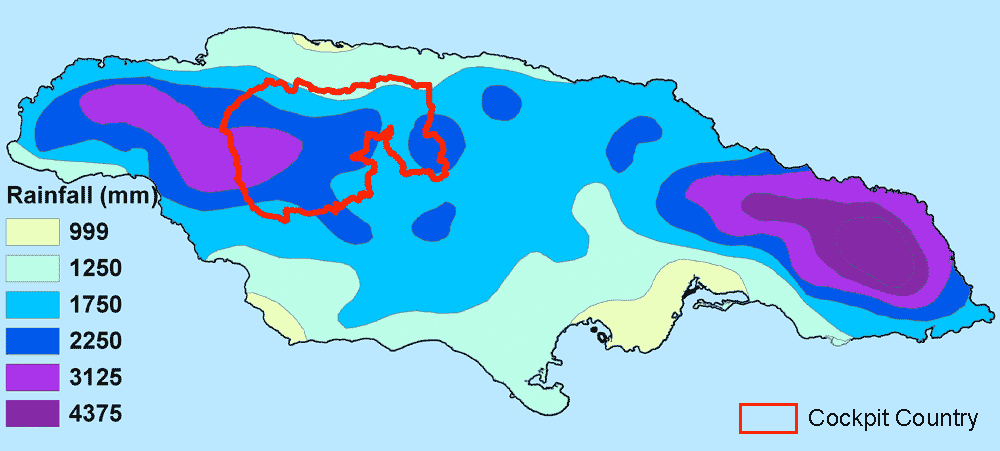
The highest rainfall totals in the Cockpit Country occur in the central core, which receives 250-380cm annually. Rainfall diminishes along the periphery to 175-250cm. There are two wet seasons in the Cockpit Country: May, which accounts for approximately 20% of total annual rainfall and September and October, which account for 27%. January and March are typically the driest months . Rainfall patterns and amounts, however, do exhibit considerable variation, particularly during El Niño Southern Oscillation cycles. On average, there are four dry months (defined as months with average rainfall less than 100 mm) annually - December to March. For an example, see Windsor rainfall
The Cockpit Country includes the upper parts of five watersheds (Black River, Great River, Montego River, Martha Brae and Rio Bueno) and recharges aquifers in all the western parishes. Karst springs well-up from the limestone aquifer predominately in the northern, lower elevation areas of the Cockpit Country . The rivers originating from the Cockpit Country account for approximately one-quarter of Jamaica's exploitable surface water runoff.
Relatively little exploitable surface water runoff is present within the Cockpit Country, a pattern characteristic of porous karst landscapes. Drainage is mostly vertical and feeds underground rivers more than 100m below ground level. These rivers may re-emerge more than 8 km from their source. There are several small rivers which emerge from blue holes and run short distances before disappearing underground, but generally the cockpits are dry or, in the case of low elevation regions, contain ponds only during the wet season. The lack of surface water has been one of the major factors that have limited the exploitation and settlement within the Cockpit Country. The limestone aquifer, however, has the capacity to contribute over 40% of the island's exploitable ground water.
We value your feedback and comments: